
Maximising Results with GHRP-6 and Ipamorelin Peptide Stacking
Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
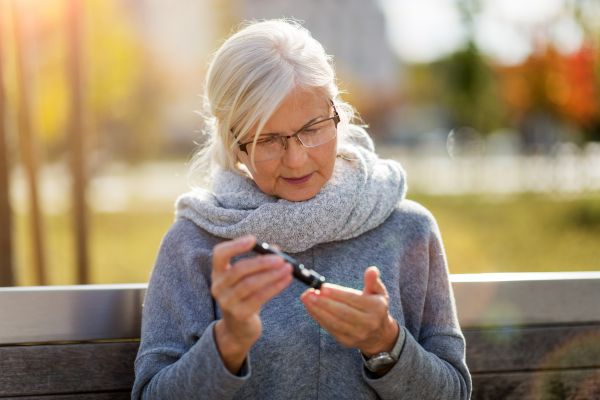

Diabetes is a chronic health condition affecting millions worldwide, characterized by the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. As such, insulin therapy is a critical component of diabetes management. However, what often goes unappreciated is the role of human C-Peptide, a molecule intertwined with insulin’s story.
This Europe blog post sails into the depths of C-Peptide’s function, its vital role in understanding and managing diabetes, and the promising avenues it offers for future research and therapeutic approaches.
C-Peptide, or connecting peptide, is a part of the insulin production process in the human body. It connects the A-chain to the B-chain in proinsulin, the precursor to active insulin. When proinsulin splits to produce insulin, C-Peptide is released into the bloodstream in equimolar amounts.
The measurement of C-peptide levels can reveal crucial information about a person’s insulin production. Low levels might indicate decreased insulin production, common in type 1 diabetes, while higher levels could suggest type 2 diabetes, where the body makes insulin but doesn’t use it effectively.
Shop Human C-Peptide online from Direct Sarms Europe today!
Insulin synthesis is a fascinating biological process that takes place within the pancreas’ beta cells. Proinsulin, with the C-Peptide, folds into a mature hormone, later cleaved to yield active insulin and C-Peptide. This conversion is essential in maintaining blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range.
Despite being side-lined as a by-product, C-Peptide isn’t without its functions. Emerging evidence suggests that it has physiological roles, such as improving blood flow and kidney function, which are of particular relevance to those with diabetes.
The link between C-Peptide and diabetes management is tightening. By measuring C-Peptide levels, medical professionals can distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, which is pivotal for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Furthermore, monitoring C-Peptide can give insights into the residual beta-cell function in diabetes patients – a critical factor in deciding whether some patients might require insulin therapy.
For individuals living with type 1 diabetes, developing therapeutic applications involving C-Peptide is a growing area of interest. Europe Research suggests that exogenous C-Peptide may alleviate some complications of diabetes, thus improving the quality of life for patients.
Noteworthy studies on C-Peptide have shed light on its potential benefits, providing impetus for continued research. Europe Clinical trials have begun exploring whether C-Peptide replacement can halt or reverse the progression of diabetes-related complications, delving into new territories of diabetes care.
These studies underline the significant promise of leveraging C-Peptide for therapeutic gains, emphasizing that this peptide might hold part of the key to unlocking better diabetes management strategies.
A deeper understanding of human C-Peptide reveals it is far more than a mere by-product of insulin production. For medical researchers, scientists, and healthcare providers, acknowledging the significance of C-Peptide levels can refine our approach to diabetes diagnosis and management.
As for Europe diabetes patients and health enthusiasts, recognising the value of C-Peptide in the body’s biochemical symphony provides a new appreciation for the intricacies of diabetes and raises hope for innovations in care and treatment.
The narrative of human C-Peptide unfolds with promising implications for the diabetic community, reinforcing the idea that thorough research and knowledge can result in life-changing breakthroughs.
In summary, C-Peptide’s narrative is not just an academic curiosity but a beacon of progress in the relentless pursuit of diabetes management and patient well-being.
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 18350117/
[2] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/ endocrinology/ articles/ 10.3389/ fendo.2023.1227260/full
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pmc/articles/PMC9367194/
[4] https://www.sciencedirect.com/ science/ article/pii/ S1550413119306242
[5] https://www.researchgate.net/ publication/235646021
Choose Direct Sarms for high quality Peptide Vials, available online today!
Disclaimer: We do not supply sarms or peptides to any individual under the age of 21. You must be a licensed and qualified healthcare practitioner. Our team of dedicated professionals are committed to providing an extensive range of products used ONLY in the process of laboratory research by responsible trained and professional individuals. All products listed on this website (direct-sarms

Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
Maximizing Healing and Rejuvenation: Exploring the Benefits of TB500 and GHK-Cu Peptides Combined In the rapidly changing field of biomedical research, peptides have become key
Worldwideshipping

Visa/Mastercard/Zelle
Cryptocurrency /Transfers

Safe and Secure Shopping

We Distribute
From

YOU MUST BE OVER 21 YEARS IN ORDER TO USE THIS WEBSITE. All of the products are to be handled only by properly trained and qualified LABORATORY or RESEARCH professionals.